"painless skin patch" is expected to provide long-term safe and personalized treatment for type 2 diabetes
Release date: 2017-12-28
“Weekly smart patches are expected to ban tedious blood sugar monitoring and insulinotropic drug taking.†Recently, research teams from China and the United States have developed a “painless skin patch†that can be used for a long time and safely. Releases incretins to regulate blood sugar balance in the body.

Currently, there are approximately 285 million people with diabetes worldwide, of which type 2 diabetes accounts for more than 90% of this group. The core of treating most type 2 diabetes is to promote insulin secretion. This "painless skin patch" has a clever "smart" design that stimulates the pancreas to produce insulin on demand, and has been validated in a mouse model.
This latest achievement was published online in the journal Nature Communications, led by Xiaoyuan Chen, a senior researcher at the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB), and Professor Fu Lijun from the Cancer Center of Sun Yat-sen University.
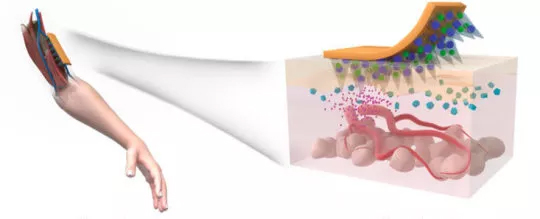
1 "smart" skin patch
"This study is based on the fact that the ability of people with type 2 diabetes to produce insulin by themselves is not completely lost," the research team said.
To achieve "intelligent" blood glucose management, the research team developed a painless skin patch that carries drugs that stimulate insulin secretion, which can be released into the blood on demand and trigger related reactions.
The painless skin patch consists of microneedles filled with alginate, a gelatinous natural substance extracted from brown algae, and mineral particles coated with the drug. “Alginate is a flexible material that is soft but not excessive and helps the particles penetrate the dermis in a non-invasive, painless form,†the researchers explained.
The mineral granules contain two drugs - Exendin-4 (Ex4) and glucose oxidase (GOx). These two compounds react with compounds in the blood to stimulate insulin secretion. The researchers wrapped the drug in phosphate mineral particles to ensure the stability of the compound.
Among them, Exendin-4 is similar in structure to glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which stimulates the release of insulin. Although the effect is weaker than natural incretin, exendin-4 remains insoluble in the blood for more than 1 hour. This means that once released from the skin patch, it can produce a lasting effect. However, once absorbed too much, exendin-4 can cause side effects such as nausea. Therefore, in order to control its absorption rate, the researchers combined it with calcium phosphate particles to ensure its stability.
Its working mechanism is also very "smart": when blood sugar rises to a precise point, phosphate will be slightly acidic under the catalysis of glucose oxidase, which stimulates the particles to release some exendin-4, which stimulates the body. Produces insulin and lowers blood sugar levels. More importantly, with the recovery of blood sugar levels, the amount of exendin-4 released will decrease until it stops.
All in all, the patch's “responsive†(intelligent) delivery system can be personalized to meet patient needs and is effective over time.
2 mouse test feasible
In a proof-of-concept experiment with a mouse model, the team found that the patch did trigger a chemical reaction in the blood, which automatically controlled blood sugar. The results showed that a one-and-a-half inch patch was able to carry a drug dose that controlled the blood glucose balance of the mice for one week.
Next, the research team plans to conduct a larger animal test. Moreover, for future clinical trials, they will also try to change the design of the patch size, needle length and so on. In addition, it is also necessary to consider the impact of sweating, showering, etc. on the patch in daily life.
Source: Bio-Exploration (micro-signal biodiscover)
Shower Gel,Shower Cream,Body Shower Gel,Foaming Shower Gel
Guangzhou Lingxue Cosmetics Co., Ltd , https://www.gzlxgj188.com
