A review of in vitro and in vivo models of colorectal cancer research
Introduction: Shanghai Jikai Gene Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. was established in 2002, has the largest lentivirus library in China, and is also the largest supplier of disease key genetic research services in China. It has accumulated more than 14 years of experimentation in the field of disease research! Here, we have compiled the experience of more than 10 research fields for everyone, and share the most practical essence with everyone! In the previous issue, I summarized the selection of in vitro and in vivo models in gastric cancer research and the application of viral tools. In this issue, let's take a look at what is special about colorectal cancer in the same digestive system.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common malignant tumors in the digestive system. In recent years, the incidence of colorectal cancer has maintained a steady growth with the improvement of living standards. Relevant data show that the incidence of colorectal cancer ranks third in the incidence of malignant tumors in China, and it is gradually increasing. Unlike lung cancer and gastric cancer, 40% to 50% of colorectal cancer patients have distant metastases at the time of initial diagnosis. Even patients who underwent radical surgical resection will eventually have more than 50% recurrence and metastasis.
Since the beginning of the 21st century, Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) targeted drugs have become a breakthrough in the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). The study of drug-related genes has also promoted the process of individualized treatment of colorectal cancer. At present, exploring the pathogenesis and metastasis mechanism of colorectal cancer, finding predictors for the efficacy of targeted monoclonal antibodies, and exploring the drug resistance mechanism represented by platinum drugs are some of the hotspots in colorectal cancer research. As the saying goes, "Knife sharply cuts the woodworker", today I will talk to you about the choice of in vitro and in vivo models in colorectal cancer research, as well as the application of virus tools.
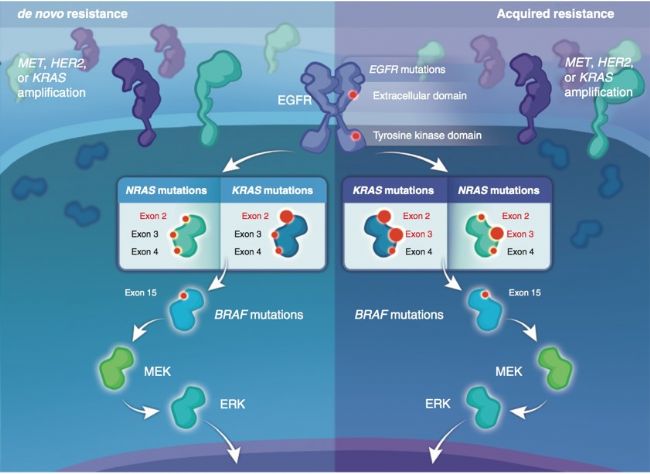
1. Which cell model do I need? Is it easy to operate?
In colorectal cancer, the direction of genomic variation has been very solid. The Kras gene mutation has been identified as a biomarker for predicting the efficacy of Cetuximab. In most other cases, mutations such as BRAF and TP53 can be found in different stages of colorectal cancer. MSI (microsatellite instability) is also a common mutation in colorectal cancer. How to make basic research closer to your clinical problems? There are two issues that must be noted: 1. Whether the cells and animal models used are consistent with the characteristics of the disease; 2. How to effectively operate the target genes in the model according to the needs of the experiment.
Come and come here, there are various cell types of colorectal cancer commonly used in molecular typing. Each cell is equipped with exclusive pre-experiment data of Jikai, so that the "variable" cells will no longer be your trouble. Come and look for Jike's watch~
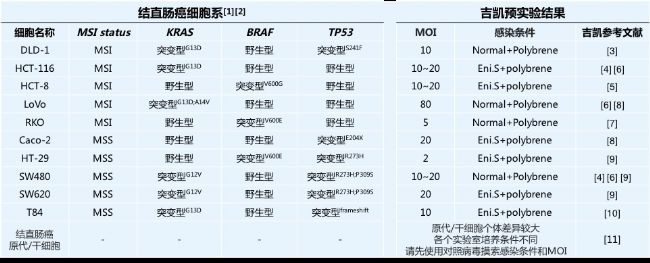

*More comprehensive pre-experiment information, please consult the local staff
Second, the cell experiment works well, how does the animal experiment do?
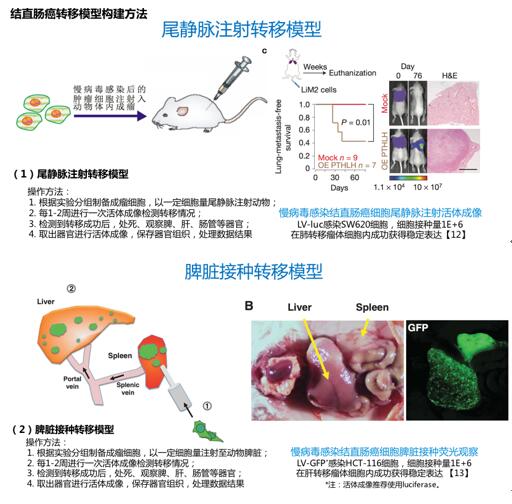
Animal models can play an important role in basic tumor research and anti-tumor research. Animal experiments in colorectal cancer research are mainly divided into three types: I spontaneous colorectal cancer model; II induced colorectal cancer model; III transplanted colorectal cancer model. The first species is mainly achieved by constructing transgenic animals, and the second species is induced by colorectal cancer using chemical inducers, but the induction model is not convenient for studying the invasion and metastasis ability of tumors; the third species directs human tumor tissues or cells directly. Inoculated in nude mice for study. Because of the low incubation conditions and hairlessness of nude mice, it is easy to observe the growth state of tumors dynamically, and the selection of inoculation methods and sites can achieve a satisfactory transfer effect. Therefore, nude mice are currently selected for human colorectal cancer cell xenograft.
According to statistics, liver metastases occur in about 30% of CRC patients, which is the leading cause of death in CRC patients. Today we will take a look at the construction of the colorectal cancer metastasis model .
Note: The in vivo model of proliferation direction is a subcutaneous tumor formation in nude mice, which is a common model for tumor research and will not be described in detail today. The experimental method can refer to the summary articles of the first two stages of lung cancer and gastric cancer.
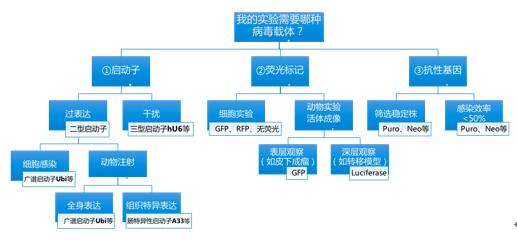
Third, the in-vivo model is selected, then what kind of chronic disease carrier does my experiment need to operate on the gene?
Promoters, fluorescent markers, and resistance tags are the three major factors we need to consider when choosing a carrier. Different components also require corresponding changes in the experiment. For intestinal cancer research, the human intestinal epithelial cell surface antigen gene A33 promoter can be used as a tissue-specific promoter. According to the example of a god figure, customizing your exclusive carrier is as simple as that!
Shanghai Jikai Gene Chemical Technology Co., Ltd. was established in 2002 and has a BSL-2 level lentivirus packaging laboratory. The virus production line has passed the ISO9001 quality management system verification, and the monthly average custom genetic virus product packaging has exceeded 1000 times. Lentiviral production uses six QC assays, viral purity fractionation and absolute quantitative detection of viral titers to ensure virus quality.
400 dedicated Jikai people, use professional to change your efficiency.
references
[1] Ahmed, D., et al. “ Epigenetic and genetic features of 24 colon cancer cell lines .†Oncogenesis 2.9 (2013): e71.
[2] Messner, Isabelle, et al. " KRAS p. G13D mutations are associated with sensitivity to anti-EGFR antibody treatment in colorectal cancer cell lines ." Journal of cancer research and clinical oncology 139.2 (2013): 201-209.
[3] Ji-Fu, E., et al. " Suppression of lung cancer metastasis-related protein 1 (LCMR1) inhibits the growth of colorectal cancer cells ." Molecular biology reports 39.4 (2012): 3675-3681.
[4] Xing, Cheng, et al. "Ubiquitin-specific protease 4-mediated deubiquitination and stabilization of PRL-3 is required for potentiating colorectal oncogenesis." Cancer research 76.1 (2016): 83-95.
[5] Yuan, Wei, et al. " Up-regulation of microRNA-145 associates with lymph node metastasis in colorectal cancer ." PloS one 9.7 (2014): e102017.
[6] Zhuang, Kangmin, et al. “ CDK5 functions as a tumor promoter in human colorectal cancer via modulating the ERK5–AP-1 axis .†Cell Death & Disease 7.10 (2016): e2415.
[7] He, Xiao-Wen, et al. " NOB1 is essential for the survival of RKO colorectal cancer cells ." World Journal of Gastroenterology: WJG 21.3 (2015): 868.
[8] Wang, Xiao, et al. “ Metalloproteases meprin-É‘ (MEP1A) is a prognostic biomarker and promotes proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer. â€BMC cancer 16.1 (2016): 383.
[9] Ji, Dengbo, et al. " MicroRNA-181a promotes tumor growth and liver metastasis in colorectal cancer by targeting the tumor suppressor WIF-1 ." Molecular cancer 13.1 (2014): 1.
[10] Huang, Huang, et al. " Regulation of TWIK-related potassium channel-1 (Trek1) restitutes intestinal epithelial barrier function ." Cellular & molecular immunology 13.1 (2016): 110-118.
[11] Leng, Zhengwei, et al. “ Krüppel-like factor 4 acts as an oncogene in colon cancer stem cell-enriched spheroid cells .†PloS one 8.2 (2013): e56082.
[12] Urosevic, Jelena, et al. " Colon cancer cells colonize the lung from established liver metastases through p38 MAPK signalling and PTHLH ." Nature cell biology 16.7 (2014): 685-694.
[13] Okamoto, Koji, et al. " miR†s induction during carcinogenesis blocks metastatic settlement of colon cancer cells in liver .†The EMBO journal 31.7 (2012): 1752-1763.

Long press and pay attention
40m Laser Distance Meter is a functional and advanced measuring tools, no need climbing up and down, which is the engineers' best friends. No matter you have your own brand or not, JRT can help you to start with laser range finder business. JRT sold more than 1 million OEM laser distance meter modules last year, and we will triple or fifth times of that quantity.
We accept OEM/ODM and customized product.
>1. Logo printed customized: at the back of the instruments etc.
>2. Distance customized: 40m, 60m, 100m, 150m.
>3. Package box customized
Distance Measure Meter,40M Laser Distance Measure,Laser Distance Meter 40M,40M Laser Distance Meter
Chengdu JRT Meter Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.rangesensors.com
